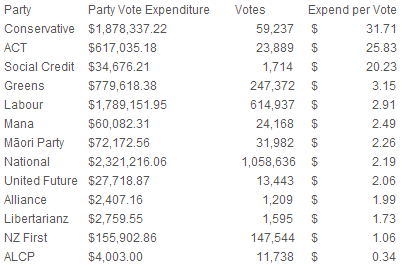
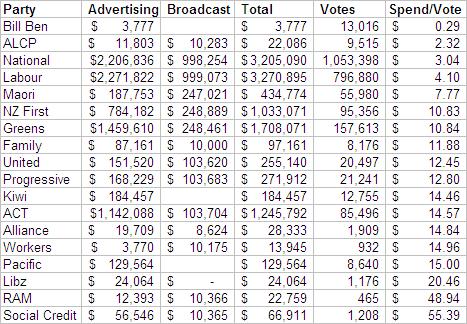
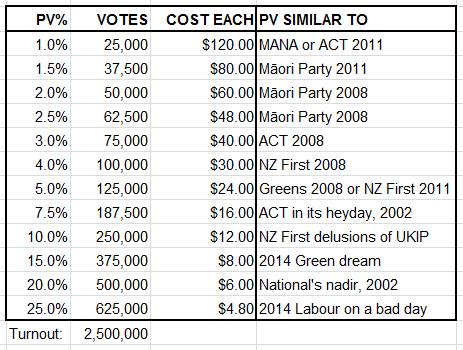
In the previous two posts I’ve covered the strategic rationales behind the Internet MANA alliance, and how, even if they spend their money very inefficiently, they are still very likely to gain a stronger presence in Parliament. But what does success actually look like for Internet MANA?
This is a complex question to answer because Internet MANA, for all its potential, is a mess of vanity projects existing in a state of ideological and pragmatic tension. But tensions all resolve sooner or later.
Kim Dotcom: Disruption (a change of government, or 10%)
Of all these vanity projects, Kim Dotcom’s is the greatest. It’s hard to imagine a guy who donated $50k to John Banks starting a cyber-utopian radical-left-aligned political vehicle for altruistic reasons, and it seems plain that he means to prevent, by any possible means, his extradition to the USA on copyright infringement and money-laundering charges. This is fair enough from his perspective — he can’t spend his pile in a US prison. NZ is a well-chosen target: a country with a small (therefore shallow, cheaply-manipulated) political system, but, unusually, also possessing a reasonably robust and independent judiciary.
To get his extradition case thrown out, Kim Dotcom needs to change the government, and prevail upon an incoming Minister of Justice that he and his party are great assets to that government.
The likelihood of this is slim, because he has already antagonised Labour, and because the leader of his own party has insisted she will not be led on the matter. Other members of the radical left groups aligned with the party are probably supportive of his ideological aim here, if only due to generalised anti-authoritarianism and anti-Americanism. And the other branch of Kim Dotcom’s game is fame, or notoriety, and if he can put his disruption engine in parliament, he will gain that, and it may provide him strategic cover for other manoeuvres regardless of who is in government.
The other way it could happen is if Internet MANA shocks everyone and polls very high — say, 10% — which would ruin almost everyone’s coalition plans. This is also extremely unlikely, but clearly it is Kim Dotcom’s hope, and it would be the purest sort of success for everyone involved.
Laila Harré: A launch (5%+) or a lifeboat (3%)
Her return to politics with the Greens last year was welcomed, and the conventional wisdom is that her appointment to lead the Internet Party was a strategic coup. I agree. But as I discussed in the first post, the deck is stacked in Te Mana’s favour. It is plausible, if the alliance performs poorly, that Harré would find herself marooned amid the wreckage of the Internet Party as its only MP, or even outside parliament, when the Internet MANA agreement expires six weeks after the election.
There’s a quirk here: Te Mana gets list places 1,3 and 4; Internet Party 2, 5 and 6, after which they alternate. So if they win five seats or fewer, Te Mana MPs will outnumber the Internet Party’s. If they win six or more seats, the numbers are more or less even. This provides a strong incentive for the Internet Party to perform, and also suggests shrewd negotiation by Te Mana.
In the event that the Internet Party bring Harré only into parliament (four seats or fewer), or if Kim Dotcom withdraws his cash and the party structure is no longer found to be self-sustaining, it seems very likely that Harré would join Te Mana formally. While her history in parties of this sort is its own guide, I suspect they would welcome her and it would be a fruitful arrangement: a win, of sorts, both for her and Te Mana.
The Internet Party: A future (7%)
The Internet Party doesn’t really exist. Kim Dotcom exists and Laila Harré exists, but without them it has no motive force. It could acquire such force by gaining a very substantial share of the party vote (7-8%, or 9-10 MPs), half of whom woulf be from the Internet Party, which could possibly — not probably — become self-sustaining. Without Laila Harré’s star power and Kim Dotcom’s money, this is a hard row for Vikram Kumar and the Candidate Idol contestants to hoe.
Te Mana and Hone Harawira: The only way is up
Te Mana’s case is easiest here: everything looks like a win for them. They have one MP facing a strong electorate challenge and polling under 1%, with no money, who is almost universally hated by the political mainstream. Even a mediocre performance of 2-3% would see Annette Sykes and possibly John Minto join Hone Harawira in parliament, which would make for some impressive fireworks. Even if the party then has to fend for itself, as Kim Dotcom’s largesse expires, or he is shipped off overseas, they have been granted a rare opportunity to galvanise the marginal electorate, and that’s better than under any other conceivable scenario.
The Left: It’s complicated
Given Labour’s current posture towards all parties that aren’t Labour, there is no way that Internet MANA benefits the left generally in the immediate term. Many commentators — Phil Quin has a good example at Pundit — have argued that the mere existence of Internet MANA could return John Key with a clean majority and the ability to have his way with Aotearoa in a glorious third term. I think this is pretty plausible. By no means does the left look like winning this election. But Labour has been underperforming for most of the past decade, and it might be that an injection of crazy disruptive ideas from a weird agglomeration of old leftwing radicals and young idealistic crypto-libertarians is what they need to shock them back to their senses.
There remains the slight possibility that they will bring enough MPs into parliament to make a chaotic and unholy alliance of the left a just slightly less-bad alternative to the Golden Age of John Key. As an aside: the better the Greens do, the better for Internet MANA post-election; and if nothing else they should hopefully form a strong ideological and generational counterpoint to New Zealand First, which I fear starts to fancy itself as the UKIP of the South Seas.
Aotearoa as a whole
I think New Zealand is better off having this argument than not. Much of what Internet MANA stands for has been unduly marginalised and is due consideration; especially the emergent aspects, such as with regard to modern standards of surveillance, the relationship and competing loyalties of the state to the citizenry and to its international community, and to the comparatively trivial matter of copyright. These debates feed into the notions of sovereignty and the primacy of people, rather than corporations and institutions, which mobilise Te Mana, and there are significant areas of ideological overlap, such as the flagship Internet Party policies of free tertiary education, withdrawal from the TPPA, severe constraints on the GCSB and other security and intelligence services, and — less popular with Hone Harawira than with his voters — the decriminalisation of marijuana. These are debates worth having, and we will be better off for having had them, whether the major parties want to or not.
L