After considerable delays related to the impact on Cyclone Gabrielle on both North Island coasts, the “A View from Afar” podcast with Selwyn Manning and I has resumed. After a brief introduction talking about the storm aftermath, we follow up the previous KP post about AUKUS, then briefly talk about the Discord classified material leaks and the power struggle in Russia. You can find the podcast here.
NZ and AUKUS PIllar 2.
As part of our preparations for the resumption of the “A View from Afar” podcasts, Selwyn Manning and I have been discussing topics for the first show. We have agreed on a micro/near-macro/far focus, with the first segment being about NZ, specifically about whether NZ should join the proposed “Pillar 2” of the recently announced AUKUS agreement that will see Australia acquire nuclear-propelled submarines based on US and UK submarine technologies. We will then move on to the impact of the Discord classified material leaks and perhaps, time permitting, what is going on in Russia recently. As part of my preparations, I shall use this post to outline some of the issues involved in NZ’s potential involvement with AUKUS Pillar 2.
AUKUS Pillar 1 involves the forward rotation of US Virginia class attack submarines based in Guam to HMAS Stirling outside of Perth, Western Australia beginning in 2027 and then the introduction of Australian nuclear-powered submarines based on the Virginia Class and UK Astute class attack submarines in the 2030s, followed by a new Australian class (the AUKUS class) in the 2040s. The SSNs (designation for nuclear powered attack submarines) will have the capability to conduct extended patrols off of New Zealand’s East Coast (which the current Collins-class diesel-electric Australian submarines cannot do) without entering NZ territorial waters (the 12 mile limit). This allows them to monitor adversary surface and submarine activity in and around NZ’s EEZ and further off-shore as well as conduct the submarine intelligence collection and intercept operations that modern submarines are primarily used for in times of peace. Undersea fiberoptic cables linking the US and Western Pacific are a major point of interest to all nations with a submarine intelligence operations capability since these are the main data exchange conduits across and within the Pacific that can be used for both offensive as well as defensive purposes in times of peace as well as war. The AUKUS submarines will certainly be used to these intelligence collection and interception ends.
It is very likely that, as has been the case with RNZAF P-3 maritime patrol and ASW aircraft in recent decades, the new RNZAF P-8 maritime patrol/ASW aircraft will be in regular contact with Australian and US naval assets, including the new RAN submarines. There is nothing new in that since the NZDF works towards seamless interoperability with Australian defense forces on land, sea and air and regularly conducts joint operations with ADF, US and other “friendly” forces across all battlefield dimensions, including tactical signals and technical intelligence. In a sense, nothing changes for NZ in terms of its defense posture now that AUKUS is in place. What does change is the modernity of the Australian naval platforms that it will be able to interact with in future operations as well as the broader range of Australian submarine coverage around all NZ shores (which in turn frees up US submarines for patrols further North in the Western Pacific). Otherwise, the current status quo remains.
For its part AUKUS Pillar 2 involves the non-nuclear, mostly economic and scientific aspects of the agreement. NZ would not have to loosen its non-nuclear status in order to participate in Pillar 2, either with regard to the submarines themselves or the land-based technologies that might be based or developed on its soil. The technologies involved include quantum computing, artificial intelligence, robotics, nano-technologies, unmanned aviation and sub-surface platforms, various sensing capabilities (e.g. acoustic, thermal, electronic, cyber) and related supply chain industries that have the potential for commercial as well as military-intelligence applications. For the Australian military industrial complex, AUKUS is a win-win. For NZ defense industrial circles, the same might apply if NZ joins Pillar 2.
When the agreement was announced Australian authorities touted the economic and scientific benefits that will accrue to Australia as a result of its signing. As the host state, Western Australia will not only see HMAS Stirling upgraded and jobs added to it in order to accomodate the presence of the nuclear submarines, but Perth and other parts of the state are envisioned to be in line to get some spill-over business in the form of input suppliers to the base. Seeing that, other Australian states have lobbied the federal government for a piece of the potential economic pie, noting for example that South Australia has a well-established boat-building capability and Victoria and New South Wales have extensive high technology sectors clustered around their main urban centres. Business leaders have joined the defense and security community in highlighting the high tech, value-added nature of both the products being developed as well as the jobs created by involvement with Pillar 2 initiatives.
Where does that leave NZ? A little while ago Minister of Defense Andrew Little said that his government “might consider” involvement in Pillar 2 once the specific details of it become known. His focus was strictly on the economic ripple effects and possible benefits to NZ of involvement in the scheme. However, in the past week Foreign Minister Nanaia Mahuta has rejected the very idea of involvement in Pillar 2, stating that policy decisions “are made by cabinet,” not by officials in the foreign or defense ministries. She went on to say that involvement in AUKUS was contrary to the “Pacific Way” of consensus building on key regional policy issues. This suggests that there is a fracture between the left and right wings of the Labour Party on the subject, something that will undoubtably come back into play as the October General Election draws closer.
We can safely assume that as a means of burnishing its conservative security and pro-business credentials, National will welcome involvement in Pillar 2 should it win in October. That is, to paraphrase notorious Iran invasion hawk Donald Rumsfeld, a “known known.” It may therefore be a better strategy for Labour to walk back its interest in Pilar 2 at least until the elections are over, if for no other reason than to not court problems with potential coalition partners like the Greens and Te Pati Maori. For their part, Australian security and business elites are unlikely to want to share the potential wealth of Pillar 2, so to speak, with NZ precisely because NZ politics is too unreliable when it comes to defense and security, especially when nuclear anything is involved. Unless Australian businesses are involved on NZ soil, why should the economic benefits of AUKUS extend beyond Australia, the US and the UK? As far as the agreement goes, NZ might as well be Canada in terms of economic involvement, and the Canadians do not constantly display a virtue signaling posture when it comes to nukes. From the standpoint of the principals involved, NZ is just trying to free-ride on their hard work.
More pointedly, as Jim Rolfe kindly alerted us in his comment below, most of what might be covered in Pillar 2 is already (at least seemingly) covered by the Five Country Technical Cooperation Program (TTCP). The TTCP is an extensive science and technology information-sharing arrangement between the 5 Eyes partners that covers a broad range of defense and intelligence-related scientific and technical subjects. Perhaps there are substantive and technical aspects to Pillar 2 that extend beyond what is covered by the TTCP remit and hence can be seen as a complement to or upgrade of already extant arrangements or a means of piggy-backing on what is already there when it comes to defense, security and intelligence industry collaboration. Remember that the pitch coming from Minister Little (as far as can be discerned) is about economic benefits that have the potential for “dual use” (i.e. military and civilian) applications, with the attendant spin-off civilian commercial effects highlighted rather than the military-security related flow-on effects per se.
One argument against NZ involvement in Pillar 2 is that it will be seen as a provocation by the PRC and thus invite retaliation. The PRC has a record for over-reacting to perceived snubs and NZ is a very dependent and hence vulnerable trade partner of it. Unlike Australia, which has strategic minerals that the PRC needs for sustain its industrial development and economic growth, NZ exports low value-added primary goods and derivatives to the PRC (think milk powders, lamb and beef, paua, crayfish and logs). When the PRC cut off Australian imports because of a diplomatic row, it went after things like wine and other non-essential goods, not the strategic minerals. NZ has no such export diversity from which to choose from when it comes to selective PRC trade sanctions, and with a third of its GDP grounded in primary good exports to the PRC, the direct and ripple effects of Chinese retaliation would be severe.
But there is a catch. The PRC already well knows which side NZ is on when it comes to international security affairs. It is well aware that NZ is part of 5 Eyes if for no other reason than the PRC is a prime target of 5 Eyes intelligence-gathering efforts, which includes a role for the NZ signals and technical intelligence agency, the GCSB. NZ has a military alliance with Australia, is a non-NATO NATO ally and has not one but two bilateral security agreements with the US (the Wellington and Washington agreements). Involvement in Pillar 2 is not necessarily an anti-PRC turn in NZ’s defense posture even if it may indirectly help the ring-fencing strategy that the US and its Pacific allies are currently undertaking vis a vis the PRC in the Western Pacific.
For the PRC, there are far more immediate concerns: the diplomatic-security (not full military) QUAD alliance involving Australia, India, Japan and the US; the recently renewed bilateral defense and security ties between the US and the Philippines, including forward basing rights for US troops as well as regular joint exercises; the change in the Japanese constitution that moves away from pacifist principles and which has facilitated a dramatic increase in defense expenditure, including on offensive weapons; the so-called US military “pivot” to the Indo-Pacific which has seen a majority of its naval assets moved into that theater along with increased numbers of amphibious troops such as the recently established US Marine expeditionary force based in Darwin and forward deployment of increased US Air Force assets in Guam; and the revitalisation of bilateral defense pacts between the US and various Southeast Asia states such as Singapore, which now has a permanent US navy presence at its naval base at Changi. There is the pushback from the US and regional allies against PRC belligerency towards Taiwan and its sovereignty-expanding island-building projects in disputed atolls across the South China Sea. The ramifications of all of these potential contingency scenarios are more pressing when it comes to Chinese military planning, so it is doubtful that NZ signing on to Pillar 2 will cause the PRC to react in an unexpected way even if it has that track record of over-reaction to perceived slights.
Plus, there is way for the PRC to exploit an advantage when it comes to NZ’s potential involvement in Pillar 2. It can use its extensive intelligence networks inside of NZ to try and obtain sensitive information about the industries and technologies involved as well as the political and military decisions that may surround them. Without firing a shot the PRC may well be able to undermine some aspects of AUKUS if it uses its intelligence assets in NZ and Australia wisely and adroitly. We can only assume that the NZ intelligence community is aware of this possibility and along with its AUKUS partners is planning counter-espionage efforts accordingly.
A significant aspect of AUKUS is that it violates the South Pacific Nuclear-Free Zone Treaty (an update of the 1986 Treaty of Rarotonga), especially Article 4 relevant to nuclear propulsion and the storage of fissile material. The stationing of the AUKUS submarines at HMAS Stirling may be an attempt to circumvent the Treat by claiming that the base is located on the Indian Ocean and outside of the SPNFZT area of coverage. But the truth is spelled out in the language of the original Treaty as well as its refinements. This is the area covered by the SPNFZT:
Should Australia breach (which is what many believe that it is doing) or renounce the SPNFZT, then it sets a precedent for other nuclear states to establish a non-weapons nuclear presence in the South Pacific if they can find a willing partner in the region (say, by forward basing a nuclear powered submarine in a Pacific Island Forum country much as the US will be doing at HMAS Stirling later this decade). The recent PRC-Solomon Islands bilateral security pact opens the door for such a possibility, and if that does in fact occur in the Solomons or elsewhere, then the taboo on stationing nuclear material of any sort in the region will have been broken.
On balance, for reasons both internal to NZ as well as those intrinsic to Australia, NZ involvement in Pillar 2 is in my opinion at least temporarily dead in the water. When it comes to high tech/value added production, perhaps NZ is better off supporting its nascent gaming, unmanned avionics and rocket booster-building industries rather than those associated with AUKUS, especially because the ripple effects of AUKUS will be felt in NZ anyway, however lightly in terms of public consumption. Moreover, with non-involvement the threat of PRC retaliation is mooted and the costs of conducting increased counter-espionage efforts against it are avoided as well.
From a political-diplomatic standpoint, Minister Mahuta may be right: NZ participation in Pillar 2 is letra morta.
” A View from Afar” returns.
On Thursday May 11, 2023 at 12PM (noon) NZ time/8PM Wed 10th May US East Coast time/1AM Thursday London time/8 AM Thursday Singapore time and 10AM Thursday Sydney time, the A View from Afar podcast will resume broadcasting. Selwyn Manning and I will discuss the AUKUS agreement and its implications for New Zealand and the fallout from the Discord classified material leaks as well as global affairs from a South Pacific perspective.
The show is interactive so tune in and join us!
Gamers, terrorists and spies.
For the better part of the last decade analysts have warned about the use of online interactive action games as a recruiting ground for white supremacists and neo-nazis (and to a lesser extent jihadists). The use of Crusader and modern Western military imagery in battles with dark skinned enemies facilitated the recruitment pitch, which given the subject material is mostly targeted at teenaged and young adult men. The policy implication of these warnings is that intelligence agencies, specifically signals and technical intelligence agencies such as those grouped in the Anglophone 5 Eyes network, need to devote resources to monitoring online gaming communities for signs of extremists and their attempts at expanding their ranks via the internet as well as formulating actual online plots to commit acts of violence.
Unfortunately most of these warnings went unheeded and continue to largely be ignored. Government intelligence agencies such as those grouped in the 5 Eyes have myriad threats and many other priorities to address besides online extremists using gaming as a recruitment portal. This has left a gap in their coverage of what is now a full fledged digital community of hate. This community does not just have gaming as a vehicle. It also includes chat and noticeboards like 4Chan and 8Chan, Reddit, Discord and other on-line communities that under the mantle of “free speech” cater to extremist viewpoints. Sadly, that attracts advertising revenue from those seeking to profit from hate and violence, be it via the sale of “hunting” weapons, uniforms, military insignia, survival gear and other para-military outfitters or publications and entities that promote ideological agendas that dovetail with the views of these types of online communities (think Voice for Freedom or Counterspin Media as NZ examples). Equally sadly, in spite of the efforts of the Christchurch Call and various advocacy groups, a majority of technology companies are loathe to self-police when it comes to issues of “free speech,” much less provide client data to security agencies in all but the most dire and pressing of circumstances.
This brings us to the subject of the recent leaks of highly classified US intelligence reports by a Massachusetts Air National Guard service member serving as an enlisted cyber transport system journeyman. In that capacity, 21 year old Airman First Class (E-3) Jack Teixeira of the 102nd Intelligence Wing of the Massachusetts Air National Guard headquartered at Joint Base Cape Cod on the site of Otis Air Field was responsible for maintaining cyber security for the Wing. In order to discharge his duties Airman Teixeira very likely was granted a Top Secret/Sensitive Compartmentalized Information (TS/SCI) security clearance that allowed him untrammelled access to what is known as a “SCIF,” a tightly secured room or building in which both paper and digital records are stored. He also had authority to visit off-station secure sites such as the Special Operations Command and other military intelligence units as part of his official duties. The US government refuses to comment on the matter of his clearances and how he obtained them pending his trial.
Using his access, as early as February 2022 Airman Teixeira began to transcribe and leak information from highly classified documents to a group of about 50 online gaming enthusiasts that were grouped in a Discord channel called “Thug Shaker Central.” He also is reported to have leaked to a larger Discord group and to forums on 4Chan and Reddit. Among these groups were a number of foreign nationals, including Russians. Two common aspects of the channels he leaked to is that they had weapons, uniform and military paraphernalia fetishes and trafficked in white supremacist, anti-Semitic, anti-Muslim, racist and misogynist narratives, with Teixeira himself now being exposed as adhering to those beliefs. The only thing missing from the profile of the gamer guys Teixeira consorted with is the label “Incel,” as in iInvoluntarily celibate. I am not sure about the others but Teixeira certainly seems to fit that bill.
At first his transcribed leaks received a lukewarm response from his (mostly younger) audience because they were pages long and covered a broad range of subjects, from details on the Russian-Ukranian War, Chinese satellite warfare plans, Taiwanese defence preparedness, Egypt’s flirtation with selling arms to the Russians, US eavesdropping on South Korean communications and much, much more. After a while, when he realised that many of the group members he was trying to impress were simply not reading his “nuggets,” he began to photograph and download the documents themselves. The would prove to be his undoing.
Transcribing the documents gave him plausible deniability because the decontextualised words (i.e., no identifying markings) could have been sourced by many people from many SCIFS. But his associates were all young male gamers who are highly visual in their information-processing, so paragraphs of words without pictures soon turned boring for them. Hence, in order to keep their attention spans focused on his “nuggets” and therefore affirm his status as leader of the Thug Shaker Central group, Teixeira needed to go digital. Once he did and the documents appeared on-line with official markings like TS/SCI and NOFORN (“No Foreign” distribution), then the counter-espionage crowd in military intelligence, the FBI and the National Security Agency (NSA) could get to work tracking him down. However, there was a twist to his uncovering. As it turns out it was the New York Times digital investigations team that first saw the documents online. Then the Washington Post was alerted to their presence. After tracing their IP addresses and social media accounts linked to them, these outlets contacted members of the Thug Shaker Command, who confirmed the legitimacy of the documents and how they came to be online. At that point the journalists contacted the US government for comment and the hunt was on. Teixeira was captured within a couple of weeks and is now awaiting trial. He faces a lengthy prison sentence and possibly a death sentence under federal espionage and treason laws. Others might find themselves arrested as well. As it stands, two commanders of the 102nd Intelligence Wing have been stood down over the breach.
Several questions have been raised as to how and why he could have been granted a high level security clearance and given so much access to sensitive information. There are also questions raised about why the chat rooms he was involved with were not being monitored by the relevant authorities and why a seemingly obscure Joint Base at an otherwise relatively quiet tourist destination be a place where deep secrets of all sorts are stored. Allow me to answer at least some of them and draw some comparisons with my own experience.
Because of the nature of his job, Teixeira required high level clearances. He comes from a Portuguese-American military family and was two years out of high school when he joined the Guard. This mitigated in his favour because it appears that he was security vetted by a contractor working for but not by a US government agency. Edward Snowden underwent the same process and we have seen how that turned out. In this case the Discord leaks are far more serious both in terms of the breadth of the subjects covered–there are more than 500 documents in the tranche realised so far- and the depth of the exposure, which includes revelation of “sources and methods.” It is not surprising that the US government has gotten rigorously quiet on the matter. Moreover, Snowden gave his purloined data files to investigative journalists and perhaps the Russian government. Teixeira put them online, where they spread from closed groups to open forums.
His family background growing up in a well-established middle class Portuguese-American community (many of the people in that part of Massachusetts and Rhode Island are descendants of Cape Verdean whalers) and his young age would have suggested to his security vettors that he had no “baggage” that could compromise national security. If they were contractors as I believe they were, he likely wouldn’t have undergone the background checks that I underwent in the 1990s by the Defense Intelligence Agency, which included polygraphs, interviews with family, friends from Argentina all the way to that current moment, work colleagues, undergraduate and graduate student peers, even my ex-wife (not surprisingly, she had little good to say about me). I was asked about my sexual preferences, political beliefs (especially whether I had ever been a member of a Communist Party), vices (gambling, alcohol, drugs, prostitutes), financial situation (especially debt) and numerous other deeply personal matters. The main concern then was two-fold: whether I could be trusted with sensitive material, and whether I could be blackmailed. My ex-wife’s opinion notwithstanding, it turns out I was pretty milquetoast as far as applicants go.
It is unlikely that a contractor would go to such lengths to establish Teixeira’s background given his age and personal life, although the apparent ignorance of his gaming activity and the fraternity of gamers that he associated with was a major lapse on the part of both the vettors as well as US signals and military intelligence agencies. However, even if he had undergone the more rigorous DIA background checks (which still exist), it would have been unlikely that, other than the gaming angle, there would have been anything alarming on his record unless he had been arrested on felony charges. He had not been. From the contractor’s point of view it made sense to go lightly on his background check, using police and FBI records and perhaps some interviews with family and friends. Since neither US intelligence agencies or the military looked into his social media and gaming profiles, there were no red flags to which the vettors could have been alerted, and they clearly did not do that sort of due diligence themselves.
The use of security vetting contractors became common place after 9/11 as the US sought to expand its intelligence networks and analyses against non-State global irregular warfare actors as well as “traditional” adversaries (and friends!). The DIA and smaller intelligence and security vetting units simply could not handle the volume of security checks required by the thousands of new hires in the intelligence-security field. There are now over 1.5 million people in the US with “Top Secret” security clearance and another 3 million with “Secret’ clearances. The solution to the overwhelming demand for background checks was to farm out the vetting to private firms with experience in the field, such as private investigation agencies or firms specifically set up by former security officials to do security vetting as their bread and butter. However, the profit motive often leads to cost-cutting when it comes to the more laborious features of the vetting process, so many firms took the cheaper way and cut corners in that regards. Investigation into the Snowden leaks uncovered that the process by which he was granted high level clearances was flawed and incomplete. It looks like the same may have happened with Airman Teixeira.
Remember that the military is a young person’s business. They do most of the killing and they are the ones who mostly die. Gaining security clearances at a young age is quite common in the US military, especially for specialised units and more so for intelligence units. Teixeira’s age was therefore not a disqualifying factor per se and again, was likely seen as a good justification for quick granting of his clearances.
What about the unit to which he was assigned? Why would it have access to such a broad array of highly classified information? The answer is that the 102nd Intelligence Wing is a renown unit with many important responsibilities. Among them, Teixera’s assigned subordinate unit, the 102nd Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance Group, processes signals and technical intelligence from U-2 spy planes, RQ-4 Global Hawk and MQ-9 Reaper drones and supports the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (from which satellite data is collected). These platforms conduct operations all over the world but specifically over Ukraine in support of the Kiev regime. Some are reported to deploy from Otis Air Field. That means that the SCIF at Joint Base Cape Cod is an integral component of US global intelligence collection activities and the US effort to support Ukraine, which justifies the presence of highly sensitive intelligence in it.
Teixeira also travelled to other SCIF sites and had opportunity to copy classified intelligence from them as well as from his home base. If he did it obviously violates his secrecy oath and sets him up for a number of serious charges. The question is whether he did so just to impress his gamer friends, or for money, or for some ideological reason. The answer is as of yet unclear. The dominant train of thought is that he is an immature young man trying to impress other younger immature men with his “insider” status as one of those who know secrets. He clearly did not do so for money. But his darker comments about race, aspects of US government policy and Russia, much of it in line with the MAGA/QAnon narrative, could point to an ideological motive. Whether that be hatred of the Deep State and Democrats or support for Russia has yet to seen.
I should point out that in my case I was sworn to not only never divulge the TS/SCI material that I handled, but also to not talking or writing without prior authorisation about the classified aspects of my government jobs for twenty years after I left public service. Anything that I did want to write or talk about in my post-government career needed to be cleared by the Defense Department, DIA or intelligence agencies that I worked with, and I was informed that anything that involved ongoing operations or assets still alive or in service would be redacted from any material I wanted to use. There were serious penalties for removing classified material from the SCIFs that I worked in (Unauthorised removal of Classified Material), and much worse, for deliberately removing classified materials in order to hand them to a third party, whomever that may be (Espionage). It will be hard for Airman Teixeira to argue that his actions were unintentional rather than deliberate, and given who were among the groups that he leaked to, it might find him facing espionage charges. The situation does not look good for him.
Whereas what attention has been brought to the online gaming community by the security agencies has focused on rightwing extremism and terrorism, it is clear that the espionage and counter-espionage aspects of interactive digital forums needs to be factored in as well. To that expansion in the scope of cyber-intelligence operations must come a thorough re-appraisal of how security background checks are conducted on people applying for high-level security clearances. This is not just a US problem. There have been enough lapses in NZ security background checks to warrant a review of current SIS procedures and processes for vetting applicants, with or without the help of consultants. Currently non-citizens can get a high level clearance if they pass the SIS checks, but here too at least some of the vetting has been contracted out to private firms (including one that was led by Michelle Boag, of all people). The issue of citizenship aside, there is enough historical evidence to suggest that the SIS (as the lead agency when it comes to security clearance vetting and background checks) might be wise to commission an independent review of its vetting procedures and operations.
Some may remember the case of the Walter Mitty-type fraudster named Stephen Wilce, the guy who claimed to have been a member of the British Olympic bobsledding team and a former SAS trooper who served as Head of the NZ Defence Technology Agency and Chief Defence Scientist from 2005 until he was exposed in 2010. He held very high level security clearances, handled very sensitive defence information and yet was vetted by an outside firm hired by the SIS. One would have thought that they might have looked up the roster of the British bobsledding team in the 1980s when he claimed to be on it, but apparently that was too much to ask. Makes one wonder where Mr. Wilce is now.
I mention this anecdote because the cyber world has opened up a whole new frontier when it comes to security and intelligence. Preventing breaches and leaks has become both easier and more difficult. Easier because the technological means to detect early online threats is greater than in previous decades. Harder because security threats have multiplied along with advancing technologies. What is needed is a proactive strategy of cyber-vigilance in conjunction with tightened requirements for background checks on those handling classified information, including monitoring social media for evidence of online extremism. Although much has been said about how the NZ Police and intelligence community are dedicating significant resources to doing so, it is telling that the Police Commissioner admitted that his agency was caught off-guard by the online planning of the Parliamentary protests last year, and in fact were unaware of the convoys that were organised via various well-known messaging applications to descend on Wellington. By the time the Police realised the size of the protest, the protestors were already setting up camp on the lawns and streets surrounding the Beehive.
Meanwhile, with that note of caution out of the way, can we all say “AI?”
The return to Big Wars.
After the Cold War the consensus among Western military strategists was that the era of Big Wars, defined as peer conflict between large states with full spectrum military technologies, was at an end, at least for the foreseeable future. The strategic emphasis shifted to so-called “small wars” and low-intensity conflicts where asymmetric warfare would be increasingly carried out by Western special forces against state and non-state actors who used irregular warfare tactics in order to compensate for and mask their comparative military weakness vis a vis large Western states. Think of the likes of Somalian militias, Indian Ocean pirates, narco-guerrillas like the Colombian FARC, ELN and Mexican cartels, al-Qaeda, ISIS/DAESH, Boko Haram, al-Shabbab, Abu Sayyaf and Hezbollah as the adversaries of that moment
Although individual Western states configured their specific interpretations of the broader strategic shift to their individual geopolitical circumstances, the broader rationale of SOLIC (Special Operations and Low Intensity Conflict) made sense. The former Soviet Union was in disarray, with Russia militarily weakened, diplomatically shrunken, economically plundered and political crippled. Its former Republics were yet unable to independently exploit their material resources, and some of its former vassal states in the Warsaw Pact were seeking NATO membership. NATO itself had lost it main purpose for being, since the threat of major war with the USSR (the original rationale for its creation) no longer existed. The PRC had yet to enjoy the economic fruits of fully embracing capitalism in order to buy, borrow and steal its way to great power status and thereby shift away from its defensive land-based strategic posture. In a swathe of regions “failed states” awash in local armed disputes replaced proxy regimes and propped up despots. In other words, there were no “big” threats that required “big” wars because there were no “peers” to fight. The strategic emphasis shifted accordingly to countering these types of threats, often under the guise of “peace-keeping” and nation-building multinational missions such as the ill-fated ISAF mission in Afghanistan.
More broadly, the strategic shift seemed right because the world had moved from a tight bipolar system during the Cold War, where the US and USSR led military blocs armed with nuclear weapons, to a unipolar system in which the US was the military, economic and political “hegemon” dominating global affairs. At the time US strategists believed that they could single-handedly prevail in 2.5 major regional wars against any adversary or combination of adversaries.That turned out to be a pipe dream but it was the order of the day until the sequels to 9/11. Even then, the so-called “war against terrorism” was asymmetric and largely low-intensity in comparative terms. Other than the initial phases of the invasion of Iraq, all other conflicts of the early 2000s have been asymmetric, with coalitions of Western actors fighting much weaker assortments of irregulars who use guerrilla tactics on land and who did not contest the air and maritime spaces around them. As has happened in the past, the longer these conflicts went on the better the chances of an “insurgent” victory. Afghanistan is the best modern example of that truism but the persistence of al-Shabbab in Northern Africa or emergence of ISIS/DAESH from the Sunni Triangle in Iraq’s Anbar Province in the aftermath of the overthrow of Saddam Hussein’s Baathist regime demonstrates the validity of the notion that guerrilla wars are best fought by insurgents as protracted wars on home terrain. In other words, apply a death by a thousand cuts strategy to foreign invaders until their will to prolong the fight is sapped.
When I was in the Pentagon in the early 1990s the joke was that bomber pilots and tank operators would need to update the resumes in order to become commercial pilots and bus or truck drivers. Money moved away from big ticket items and into the SOLIC community, with a rapid expansion of SEAL, Green Beret, Ranger and Marine Recon units designed to operate in small group formations behind or within enemy lines for extended periods of time. If the Big War moment culminated in “Shock and Awe,” the SOLIC strategy was two pronged when it came to counter-insurgency (COIN) objectives: either decapitation strikes against “high value targets” or a hearts and minds campaign in which cultural operations (such as building schools, bridges and toilets) supplemented kinetic operations led by allied indigenous forces using the elements of military superiority provided by Western forces. This required familiarisation with local cultures and indigenous terrain, so investment in language training and anthropological and sociological studies of societies in which the SOLIC units operated was undertaken, something that was not a priority under Big War strategies because the objective there is to kill enemies and incapacitate their war effort as efficiently as possible, not to understand their culture or their motivations.
SOLIC turned out to be a mixed bag. The US and its allies found out, yet again, that much as like in Viet Nam, indigenous guerrilla forces were often ingenious, inspired and persistent. They learned to get out of the way when Western forces were massed against them, and they knew how to utilise hit and run tactics to frustrate their enemies. It was only when they made mistakes, like ISIS/DAESH’s attempt to create a territorially based Caliphate in Northern Irag and Northern Syria, and then engaged in a protracted defence of its base city Mosul, that they were decisively defeated. Even then remnants of this group and others continue to regroup and return to the fight even after suffering tremendous setbacks on the battlefields. As the saying goes, it is not who suffers the least losses that wins the fight, but instead it is those who can sustain the most losses and keep on fighting that ultimately prevail in a protracted irregular warfare scenario. Again, the Taliban prove the point.
During the time that the West was engaged in its SOLIC adventures, the PRC, Russia and emerging powers like India invested heavily in military modernisation and expansion programs. While the US and its allies expended blood and treasure on futile efforts to bring democracy to deeply entrenched authoritarian societies from the barrel of a gun, emerging great powers concentrated their efforts on developing military power commensurate with their ambitions. Neither the PRC, Russia or India did anything to support the UN mandates authorising armed interventions in Iraq and Afghanistan, and in fact Russia and the PRC funnelled small arms to the Taliban via Pakistan, another yet nuclear armed but unstable state whose utility lies in its strategic ambiguity when it comes to big power conflicts. That fence-straddling posture will eventually be called.
However the future specifics unfold, that move to new or renewed militarisation was an early sign that the unipolar moment was coming to an end and that a multipolar order was in the making. Meanwhile, politics in the West turned inwards and rightwards, the US withdrew from Iraq and ten years later from Afghanistan without making an appreciable difference on local culture and society, with the entire liberal democratic world responding weakly to the PRC’s neo-imperialist behaviour in its near abroad and increasing Russian bellicosity with regards to former Soviet states, Georgia and Ukraine in particular (to say nothing of their direct influence operations and political interference in places like the US, UK, Germany and Australia). The challenges to US “hegemony” were well underway long before Donald Trump dealt US prestige and power a terminal blow.
Things on the strategic front came to a head when Russia invaded Ukraine in February 2022. The West and NATO had responded weakly to the annexation of the Donbas region and Crimea by pro-Russian separatists and Russian “Green Men” ( professional soldiers in green informs without distinctive insignia) in 2014. The same had occurred in Georgia in 2008, when Russian forces successfully backed pro-Russian irredentist groups in the Georgian provinces of South Ossetia and Abkhazia. Vladimir Putin read the West’s response to these two incursions as a sign of weakness and division within NATO and the liberal democratic world in general. He figured that an invasion of Ukraine would be quick and relatively painless because many Ukrainians are of Russian descent and would welcome his troops and prefer to be part of Mother Russia rather than a Ukrainian government presided over by a comedian. NATO and the US would dither and divide over how to respond and Russia would prevail with its land grab. And then, of course, Russia has a legion of hackers dedicated to subverting Western democracy in cyberspace and on social media (including in NZ) and better yet, has acolytes and supporters in high places, particularly in the US Republican Party and conservative political movements the world over.
In spite of all of these points of leverage, none of the Kremlin’s assumptions about the invasion turned out to be true. Russian intelligence was faulty, framed to suit Putin’s vainglorious desires rather than objectively inform him of what was awaiting his forces. Instead of a walk-over, the invasion stiffened Ukrainian resolve, ethnic Russians in Ukraine did not overwhelmingly welcome his troops and instead of dividing, NATO reunified and even has begin to expand with the upcoming addition of Finland and Sweden now that the original threat of the Russian Bear (and the spectre of the USSR) is back as the unifying agent.
Meanwhile the PRC has increased its threats against Taiwan, completely militarised significant parts of the South China Sea, encroached on the territorial waters and some island possessions of neighbouring littoral states, engaged in stealthy territorial expansion in places like Bhutan, clashed with Indian forces in disputed Himalayan territory and cast a blind eye on the provocative antics of its client state, North Korea. It has used soft power and direct influence campaigns, including wide use of bribery, to accrue influence in Africa, Latin America and the South Pacific. It arms Iran, Cuba, Venezuela and Nicaragua in spite of their less than splendid regime characteristics. It violates international treaties and conventions such as the Law of the Sea, the sovereignty of airspace over other nation’s territories and various fishery protection compacts. It uses its state-backed companies for espionage purposes, engages in industrial espionage and intellectual property theft on grand scale and acts like an environmental vandal in its quest for raw material imports from other parts of the world (admittedly, it is not alone in this). It does not behave, in other words as a responsible, law-abiding international citizen. And it is now armed to the teeth, including a modernised missile fleet that is clearly designed to be used against US forces in the Western Pacific and beyond, including the US mainland if nuclear war becomes a possibility.
All of this sabre rattling and actual war-mongering by the PRC, Russia and allies like Iran and North Korea were reason enough for Western strategists to reconsider the Big War thesis. But it is the actual fighting in Ukraine that has jolted analysts to re-valuing full spectrum warfare from the seabed to outer space.
Since 2016 the US Defense Department has begin to shift its strategic gaze towards fighting Big Wars. In its 2022 National Defense Strategy and related documents, this orientation is explicit, mentioning north the PRC and Russia as main threats.For its part, the PRC has responded in kind and warns that US “interventionism” will pay a heavy price should it interfere with China’s rightful claims on its near abroad (which on Chinese maps extend well into the Pacific). The DPRK is accelerating its ballistic missile tests and openly talking about resuming nuclear warhead testing. India is going full bore with aircraft carrier and submarine fleet expansion. Germany is re-arming as its supplies Ukraine with increasingly sophisticated battle systems while the UK and Australia are raising their defense spending above 2 percent of GDP (the much vaunted but until recently ignored NATO standard). France has withdrawn from its SOLIC operations in North and Central Africa in order to prepare for larger conflicts involving its core interests. Japan has revised its long-standing pacifist constitution and has begun to add offensive weapons into its inventory as well as more closely integrating with the 5 Eyes Anglophone signals intelligence network.
The arms race is on and the question now is whether a security dilemma is being created that will lead to a devastating miscalculation causing a major war (security dilemmas are a situation where one State, seeing that a rival State is arming itself seemingly out of proportion to its threat environment, begins to arm itself in response, thereby prompting the rival State to increase its military expenditures even more, leading to a spiralling escalation of armament purchases and deployments that at some point can lead to a misreading of a situation and an armed clash that in turn escalates into war).
The race to the Big War is also being fuelled by middle powers like those of the Middle East (Israel included) and even Southeast Asia, where States threatened by Chinese expansionism are doubling down on military modernisation programs. A number of new security agreements such as the Quad and AUKUS have been signed into force, exacerbating PRC concerns that its being ring-fenced by hostile Western adversaries and their Asian allies. As another saying goes, “perception is everything.”
None of this means that large States will abandon SOLIC anytime soon. Special forces will be used against armed irregular groups throughout the world as the occasion requires. But in terms of military strategic doctrines, all of the major powers are now preparing for the next Big War. That is precisely why alliances are being renewed or created, because allied firepower is a force multiplier that can prove decisive in the battle theater.
One thing needs to be understood about Big Wars. The objective is that they be short and to the point. That is, overwhelming force is applied in the most efficient way in order to break the enemy’s physical capabilities and will to fight in the shortest amount of time. Then a political outcome is imposed. What military leaders do not want is what is happening to the Russians in Ukraine: bogged down by a much smaller force fighting on home soil with the support of other large States that see the conflict as a proxy for the real thing. The idea is get the fight over with as soon as possible, which means bringing life back to the notion of “overwhelming force,” but this time against a peer competitor.
The trickle down effects of this strategic shift are being felt in Australasia. Singapore has agreed to hosting forward basing facilities for a US littoral combat ship and its shore-based complement as well as regular port calls by US Navy capital ships such as aircraft carriers. The Philippines have renewed a bilateral defense pact with the US after years of estrangement. Australia has aligned its strategic policy with that of the US and with the signing of the AUKUS agreement on nuclear-powered submarines and adjacent military technologies has become a full fledged US military ally across the leading edges of military force (Australia will now become only the second nation that the US shares nuclear submarine technologies with, after the UK). Even New Zealand is making the shift, with recent Defense White Papers and other command announcements all framing the upcoming strategic environment as one involving great power competition (in which the PRC is seen as the regional disruptor) with the potential for conflict in the South and Western Pacific (with a little concern about the adverse impact of climate change of Pacific communities thrown in). In other words, the times they are a’changin’ in New Zealand’s strategic landscape. For NZ, comfort of being in a benign strategic environment no longer applies.
It remains to be seen how long New Zealand’s foreign policy elite fully comprehend what their military commanders are telling them about what is on the strategic horizon. They may well still cling to the idea that they can trade preferentially with the PRC, stay out of Russian inspired conflicts and yet receive full security guarantees from its Anglophone partners. But if they indeed think that way, they are in for an unpleasant surprise because one way or another NZ will be pulled into the next Big War whether it likes it or not.
On the darkness behind the PM’s departure.
Over the weekend I was interviewed by a media outlet about the threats that Jacinda Ardern and her family have received while she has been PM and what can be expected now that she has resigned. I noted that the level of threat she has been exposed to is unprecedented in NZ history, something that is due not as much as to the content of her policies (especially but not exclusively the pandemic mitigation measures and 3 Waters initiative), but to the social media megaphoning of (often foreign imported) conspiracy theories and anti-government sentiment that used her policies as an excuse to engage in extremely misogynistic and violent verbal attacks and physical threats against her. The 2022 Parliamentary Protests represented the NZ January 6 moment in terms of crystallising the focused hatred of the assortment of seditionists assembled in one place (including Nazi imagery superimposed on the PMs face and nooses hung with placards calling for her and other politician’s executions), but their threats will not go away just because she has left office.
The original story got picked up by other outlets that include overseas media platforms. The response has been mixed. Although commentary has often sided with my view that the hatred directed at Ms. Ardern is unprecedented in NZ, a large number of pundits have proved my point by repeating the threats as well as justifications for them (“she reaps what she sowed,” “she deserves it,” “the penalty for treason is death,” “she created a two tier society,” “what is good for the goose is good for the gander,” “she is a Satanist globalist freemason Big Pharma puppet intent on destroying the Kiwi way of life” and so much more along such lines. The authors of these nuggets of brilliance walk amongst us.
I decided to throw together a couple of tweets on the business account to note two points of interest. They are “If Jacinda Ardern’s resignation sparks a national discussion about gendered abuse and violence in Aotearoa in general and against females/women in positions of authority in particular (political as well as elsewhere), then it will have been a fitting parting gesture on her part. But that will not be the end of it for her.” (I added the term “women” here because some po-mo people objected to the term “female” in the original post).
And (on the issue of the threat environment she must confront): “One measure of the threat landscape that Jacinda Ardern has had to traverse is the personal security detail she and her family will need after she leaves public life. Our reckon is that it will be significant, at least over the short term.” That brought a number of responses, some of which questioned how things got to this point and whether I was exaggerating what could be just foreign threats or blowhard ranting here at home. My response:
“When threat assessing, there are perpetrators, accomplices, enablers, subjects and objects. NZ is full of media (social and corporate) accomplices and enablers when it comes to subjecting Ardern to violent intimidation by a dangerous local fringe (the object). The danger is here.” To elaborate: threat assessment is about establishing a hierarchy of actors and their potential for action, then determining what action they are likely to take and how realistic and imminent is the possibility/probability of their turning words into action. In the case of Jacinta Ardern, I do not believe that the threats to her and her family will go away just because she has stepped down. And given that the Police have eight active investigations into individuals who have made such threats and because I believe that they are just the tip of a threat pyramid that is real and imminent, I continue to stand by these statements.
I could go on to elaborate on what I said in the original interview and follow ups but the story is now viral and can be better accessed by search for the coverage itself.
Suffice to say, this not a good moment for the former PM but also for the country as a political society, and that has nothing to do with her policies or behaviour in office but all to do with those who began and those who then facilitated the mainstreaming of extremist discourse into corporate media narratives and coverage of her government’s policies. Between social media networked nastiness and corporate media megaphoning and legitimating of previously fringe views untethered to reality, the moment is, to paraphrase Gramsci,” delicate and dangerous.”
In this election year more than any other time, especially because of the delicacy of the moment, that is a syndrome that must be remembered and confronted.
A Note of Caution.
The repeal of Roe vs Wade by the US Supreme Court is part of a broader “New Conservative” agenda financed by reactionary billionaires like Peter Thiel, Elon Mush, the Kochs and Murdochs (and others), organised by agitators like Steve Bannon and Rodger Stone and legally weaponised by Conservative (often Catholic) judges who are Federalist Society members. The agenda, as Clarence Thomas openly (but partially) stated, is to roll back the rights of women, ethnic and sexual minorities as part of an attempt to re-impose a heteronormative patriarchal Judeo-Christian social order in the US.
Worse, the influence of these forces radiates outwards from the US into places like NZ, where the rhetoric, tactics and funding of rightwing groups increasingly mirrors that of their US counterparts. Although NZ is not as institutionally fragile as the US, such foreign influences are corrosive of basic NZ social values because of their illiberal and inegalitarian beliefs. In fact, they are deliberately seditious in nature and subversive in intent. Thus, if we worry about the impact of PRC influence operations in Aotearoa, then we need to worry equally about these.
In fact, of the two types of foreign interference, the New Conservative threat is more immediate and prone to inciting anti-State and sectarian violence. Having now been established in NZ under the mantle of anti-vax/mask/mandate/”free speech” resistance, it is the 5th Column that needs the most scrutiny by our security authorities.
Media Link: “A View from Afar” on NATO and BRICS Leader’s summits.
Selwyn Manning and I discussed the upcoming NATO Leader’s summit (to which NZ Prime Minister Ardern is invited), the rival BRICS Leader’s summit and what they could mean for the Ruso-Ukrainian Wa and beyond.
The PRC’s Two-Level Game.
Coming on the heels of the recently signed Solomon Islands-PRC bilateral economic and security agreement, the whirlwind tour of the Southwestern Pacific undertaken by PRC Foreign Minister Wang Yi has generated much concern in Canberra, Washington DC and Wellington as well as in other Western capitals. Wang and the PRC delegation came to the Southwestern Pacific bearing gifts in the form of offers of developmental assistance and aid, capacity building (including cyber infrastructure), trade opportunities, economic resource management, scholarships and security assistance, something that, as in the case of the Solomons-PRC bilateral agreement, caught the “traditional” Western patrons by surprise. With multiple stops in Kiribati, Fiji, Samoa, Tonga, PNG, Vanuatu and East Timor and video conferencing with other island states, Wang’s visit represents a bold outreach to the Pacific Island Forum community.
A couple of days ago I did a TV interview about the trip and its implications. Although I posted a link to the interview, I thought that I would flesh out was what unsaid in the interview both in terms of broader context as well as some of the specific issues canvassed during the junket. First, in order to understand the backdrop to recent developments, we must address some key concepts. Be forewarned: this is long.
China on the Rise and Transitional Conflict.
For the last three decades the PRC has been a nation on the ascent. Great in size, it is now a Great Power with global ambitions. It has the second largest economy in the world and the largest active duty military, including the largest navy in terms of ships afloat. It has a sophisticated space program and is a high tech world leader. It is the epicenter of consumer non-durable production and one of the largest consumers of raw materials and primary goods in the world. Its GDP growth during that time period has been phenomenal and even after the Covid-induced contraction, it has averaged well over 7 percent yearly growth in the decade since 2011.
The list of measures of its rise are many so will not be elaborated upon here. The hard fact is that the PRC is a Great Power and as such is behaving on the world stage in self-conscious recognition of that fact. In parallel, the US is a former superpower that has now descended to Great Power status. It is divided domestically and diminished when it comes to its influence abroad. Some analysts inside and outside both countries believe that the PRC will eventually supplant the US as the world’s superpower or hegemon. Whether that proves true or not, the period of transition between one international status quo (unipolar, bipolar or multipolar) is characterised by competition and often conflict between ascendent and descendent Great Powers as the contours of the new world order are thrashed out. In fact, conflict is the systems regulator during times of transition. Conflict may be diplomatic, economic or military, including war. As noted in previous posts, wars during moments of international transition are often started by descendent powers clinging or attempting a return to the former status quo. Most recently, Russia fits the pattern of a Great Power in decline starting a war to regain its former glory and, most importantly, stave off its eclipse. We shall see how that turns out.
Spheres of Influence.
More immediate to our concerns, the contest between ascendent and descendent Great Powers is seen in the evolution of their spheres of influence. Spheres of influence are territorially demarcated areas in which a State has dominant political, economic, diplomatic and military sway. That does not mean that the areas in question are as subservient as colonies (although they may include former colonies) or that this influence is not contested by local or external actors. It simply means at any given moment some States—most often Great Powers—have distinct and recognized geopolitical spheres of influence in which they have primacy of interest and operate as the dominant regional actor.
In many instances spheres of influence are the object of conquest by an ascendent power over a descendent power. Historic US dominance of the Western Hemisphere (and the Philippines) came at the direct expense of a Spanish Empire in decline. The rise of the British Empire came at the expense of the French and Portuguese Empires, and was seen in its appropriation of spheres of influence that used to be those of its diminished competitors. The British and Dutch spheres of influence in East Asia and Southeast Asia were supplanted by the Japanese by force, who in turn was forced in defeat to relinquish regional dominance to the US. Now the PRC has made its entrance into the West Pacific region as a direct peer competitor to the US.
Peripheral, Shatter and Contested Zones.
Not all spheres of influence have equal value, depending on the perspective of individual States. In geopolitical terms the world is divided into peripheral zones, shatter zones and zones of contestation. Peripheral zones are areas of the world where Great Power interests are either not in play or are not contested. Examples would be the South Pacific for most of its modern history, North Africa before the discovery of oil, the Andean region before mineral and nitrate extraction became feasible or Sub-Saharan Africa until recently. In the modern era spheres of influence involving peripheral zones tend to involve colonial legacies without signifiant economic value.
Shatter zones are those areas where Great Power interests meet head to head, and where spheres of influence clash. They involve territory that has high economic, cultural or military value. Central Europe is the classic shatter zone because it has always been an arena for Great Power conflict. The Middle East has emerged as a potential shatter zone, as has East Asia. The basic idea is that these areas are zones in which the threat of direct Great Power conflict (rather than via proxies or surrogates) is real and imminent, if not ongoing. Given the threat of escalation into nuclear war, conflict in shatter zones has the potential to become global in nature. That is a main reason why the Ruso-Ukrainian War has many military strategists worried, because the war is not just about Russia and Ukraine or NATO versus Russian spheres of influence.
In between peripheral and shatter zones lie zones of contestation. Contested zones are areas in which States vie for supremacy in terms of wielding influence, but short of direct conflict. They are often former peripheral zones that, because of the discovery of material riches or technological advancements that enhance their geopolitical value, become objects of dispute between previously disinterested parties. Contested zones can eventually become part of a Great Power’s sphere of influence but they can also become shatter zones when Great Power interests are multiple and mutually disputed to the point of war.
Strategic Balancing.
The interplay of States in and between their spheres of influence or as subjects of Great Power influence-mongering is at the core of what is known as strategic balancing. Strategic balancing is not just about relative military power and its distribution, but involves the full measure of a State’s capabilities, including hard, soft, smart and sharp powers, as it is brought to bear on its international relations.
That is the crux of what is playing out in the South Pacific today. The South Pacific is a former peripheral zone that has long been within Western spheres of influence, be they French, Dutch, British and German in the past and French, US and (as allies and junior partners) Australia and New Zealand today. Japan tried to wrest the West Pacific from Western grasp and ultimately failed. Now the PRC is making its move to do the same, replacing the Western-oriented sphere of influence status quo with a PRC-centric alternative.
The reason for the move is that the Western Pacific, and particularly the Southwestern Pacific has become a contested zone given technological advances and increased geopolitical competition for primary good resource extraction in previously unexploited territories. With small populations dispersed throughout an area ten times the size of the continental US covering major sea lines of communication, trade and exchange and with valuable fisheries and deep water mineral extraction possibilities increasingly accessible, the territory covered by the Pacific Island Forum countries has become a valuable prize for the PRC in its pursuit of regional supremacy. But in order to achieve this objective it must first displace the West as the major extra-regional patron of the Pacific Island community. That is a matter of strategic balancing as a prelude to achieving strategic supremacy.
Three Island Chains and Two Level Games.
The core of the PRC strategy rests in a geopolitical conceptualization known as the “three island chains” This is a power projection perspective based on the PRC eventually gaining control of three imaginary chains of islands off of its East Coast. The first island chain, often referred to those included in the PRC’s “Nine Dash Line” mapping of the region, is bounded by Japan, Northwestern Philippines, Northern Borneo, Malaysia and Vietnam and includes all the waters within it. These are considered to be the PRC’s “inner sea” and its last line of maritime defense. This is a territory that the PRC is now claiming with its island-building projects in the South China Sea and increasingly assertive maritime presence in the East China Sea and the straits connecting them south of Taiwan.
The second island chain extends from Japan to west of Guam and north of New Guinea and Sulawesi in Indonesia, including all of the Philippines, Malaysian and Indonesian Borneo and the island of Palau. The third island chain, more aspirational than achievable at the moment, extends from the Aleutian Islands through Hawaii to New Zealand. It includes all of the Southwestern Pacific island states. It is this territory that is being geopolitically prepared by the PRC as a future sphere of influence, and which turns it into a contested zone.
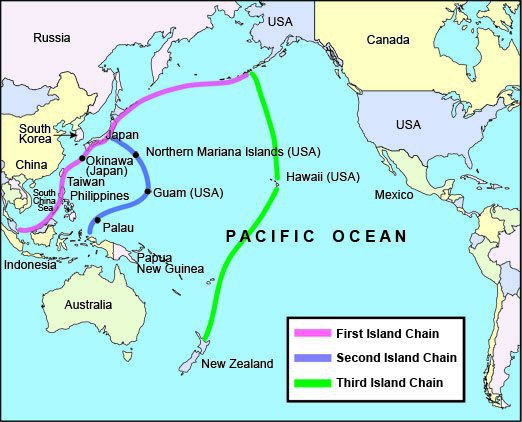
(Source: Yoel Sano, Fitch Solutions)
The PRC approach to the Southwestern Pacific can be seen as a Two Level game. On one level the PRC is attempting to negotiate bilateral economic and security agreements with individual island States that include developmental aid and support, scholarship and cultural exchange programs, resource management and security assistance, including cyber security, police training and emergency security reinforcement in the event of unrest as well as “rest and re-supply” and ”show the flag” port visits by PLAN vessels. The Solomon Island has signed such a deal, and Foreign Minister Wang has made similar proposals to the Samoan and Tongan governments (the PRC already has this type of agreement in place with Fiji). The PRC has signed a number of specific agreements with Kiribati that lay the groundwork for a more comprehensive pact of this type in the future. With visits to Vanuatu, Papua New Guinea and East Timor still to come, the approach has been replicated at every stop on Minister Wang’s itinerary. Each proposal is tailored to individual island State needs and idiosyncrasies, but the general blueprint is oriented towards tying development, trade and security into one comprehensive package.
None of this comes as a surprise. For over two decades the PRC has been using its soft power to cultivate friends and influence policy in Pacific Island states. Whether it is called checkbook or debt diplomacy (depending on whether developmental aid and assistance is gifted or purchased), the PRC has had considerable success in swaying island elite views on issues of foreign policy and international affairs. This has helped prepare the political and diplomatic terrain in Pacific Island capitals for the overtures that have been made most recently. That is the thrust of level one of this strategic game.
That opens the second level play. With a number of bilateral economic and security agreements serving as pillars or pilings, the PRC intends to propose a multinational regional agreement modeled on them. The first attempt at this failed a few days ago, when Pacific Island Forum leaders rejected it. They objected to a lack of detailed attention to specific concerns like climate change mitigation but did not exclude the possibility of a region-wide compact sometime in the future. That is exactly what the PRC wanted, because now that it has the feedback to its initial, purposefully vague offer, it can re-draft a regional pact tailored to the specific shared concerns that animate Pacific Island Forum discussions. Even if its rebuffed on second, third or fourth attempts, the PRC is clearly employing a “rinse, revise and repeat” approach to the second level aspect of the strategic game.
An analogy the captures the PRC approach is that of an off-shore oil rig. The bilateral agreements serve as the pilings or legs of the rig, and once a critical mass of these have been constructed, then an overarching regional platform can be erected on top of them, cementing the component parts into a comprehensive whole. In other words, a sphere of influence.

Western Reaction: Knee-Jerk or Nuanced?
The reaction amongst the traditional patrons has been expectedly negative. Washington and Canberra sent off high level emissaries to Honiara once the Solomon Islands-PRC deal was leaked before signature, in a futile attempt to derail it. The newly elected Australian Labor government has sent its foreign minister, sworn into office under urgency, twice to the Pacific in two weeks (Fiji, Tonga and Samoa) in the wake of Minister Wang’s visits. The US is considering a State visit for Fijian Prime Minister (and former dictator) Frank Baimimarama. The New Zealand government has warned that a PRC military presence in the region could be seriously destabilising and signed on to a joint US-NZ statement at the end of Prime Minister Ardern’s trade and diplomatic junket to the US re-emphasising (and deepening) the two countries’ security ties in the Pacific pursuant to the Wellington and Washington Agreements of a decade ago.
The problem with these approaches is two-fold, one general and one specific. If countries like New Zealand and its partners proclaim their respect for national sovereignty and independence, then why are they so perturbed when a country like the Solomon Islands signs agreements with non-traditional patrons like the PRC? Besides the US history of intervening in other countries militarily and otherwise, and some darker history along those lines involving Australian and New Zealand actions in the South Pacific, when does championing of sovereignty and independence in foreign affairs become more than lip service? Since the PRC has no history of imperialist adventurism in the South Pacific and worked hard to cultivate friends in the region with exceptional displays of material largesse, is it not a bit neo-colonial paternalistic of Australia, NZ and the US to warn Pacific Island states against engagement with it? Can Pacific Island states not find out themselves what is in store for them should they decide to play the Two Level Game?
More specifically, NZ, Australia and the US have different security perspectives regarding the South Pacific. The US has a traditional security focus that emphasises great power competition over spheres of influence, including the Western Pacific Rim. It has openly said that the PRC is a threat to the liberal, rules-based international order (again, the irony abounds) and a growing military threat to the region (or at least US military supremacy in it). As a US mini-me or Deputy Sheriff in the Southern Hemisphere, Australia shares the US’s traditional security perspective and emphasis when it comes to threat assessments, so its strategic outlook dove-tails nicely with its larger 5 Eyes partner.
New Zealand, however, has a non-traditional security perspective on the Pacific that emphasises the threats posed by climate change, environmental degradation, resource depletion, poor governance, criminal enterprise, poverty and involuntary migration. As a small island state, NZ sees itself in a solidarity position with and as a champion of its Pacific Island neighbours when it comes to representing their views in international fora. Yet it is now being pulled by its Anglophone partners into a more traditional security perspective when it comes to the PRC in the Pacific, something that in turn will likely impact on its relations with the Pacific Island community, to say nothing of its delicate relationship with the PRC.
In any event, the Southwestern Pacific is a microcosmic reflection of an international system in transition. The issue is whether the inevitable conflicts that arise as rising and falling Great Powers jockey for position and regional spheres of influence will be resolved via coercive or peaceful means, and how one or the other means of resolution will impact on their allies, partners and strategic objects of attention such as the Pacific Island community.
In the words of the late Donald Rumsfeld, those are the unknown unknowns.
Media Link: China in the Pacific.
I got up early to do a TV interview about the recent (and ongoing) trip by the PRC foreign minister around the SW Pacific looking to sign bilateral and multilateral agreements. I never got to discuss the concept of “sphere of influence” as it applies to the power play, nor the fact that the territorial size and resource exploitation potential of any potential PRC-Pacific Island community multilateral economic and security agreement would mark a major shift in the Pacific strategic balance of power. But I did get to try and put the recent moves in broader context, which is unusual for a TV talking head. You can see the interview here.
